Key Takeaway
Manual lymphatic drainage is safe and may offer additional benefit when combined with compression therapy for lymphedema management.
Summary
This Cochrane systematic review examined the evidence for manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) in treating lymphedema following breast cancer treatment. MLD is a gentle massage technique that stimulates lymphatic flow.
The review found that MLD is safe and when combined with compression bandaging, may provide modest additional benefit over compression alone. The quality of evidence was low due to methodological limitations in available trials.
While focused on clinical lymphedema, this review establishes that manual lymphatic stimulation can meaningfully affect lymphatic function.
Methods
- Cochrane systematic review methodology
- Randomized controlled trials of MLD
- Comparison to standard care or compression
- Multiple outcome measures (limb volume, quality of life)
Key Results
- MLD is safe with no adverse effects reported
- Modest additional benefit when combined with compression
- Some improvement in quality of life outcomes
- Effects more pronounced in mild-to-moderate lymphedema
Figures
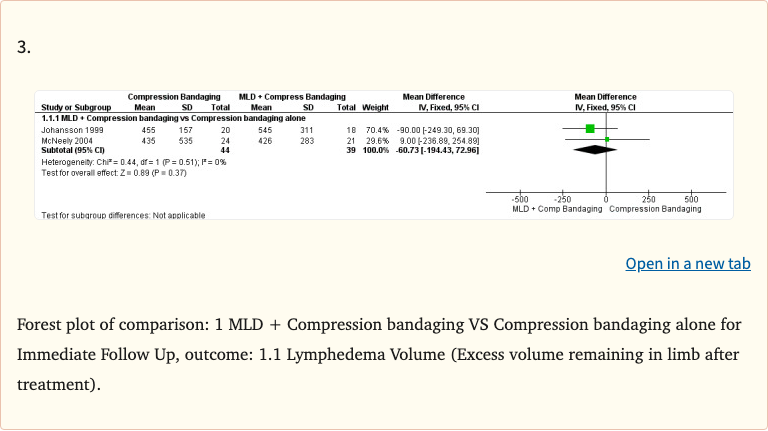 Figure 1
Figure 1
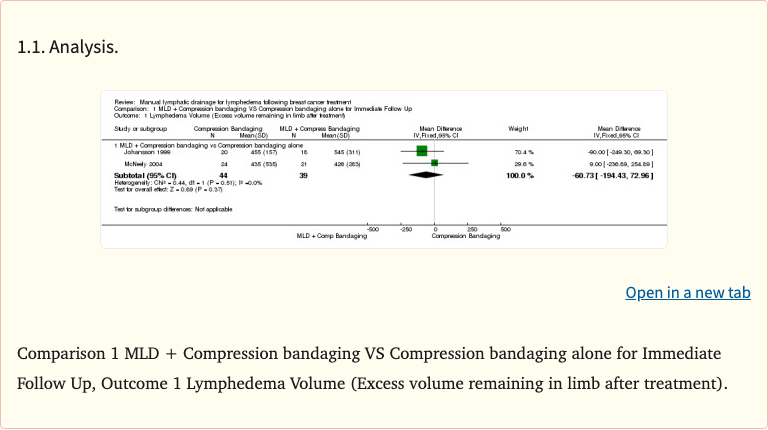 Figure 2
Figure 2
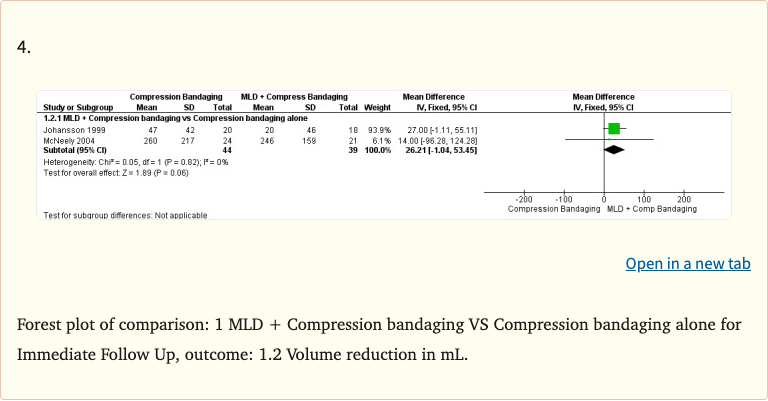 Figure 3
Figure 3
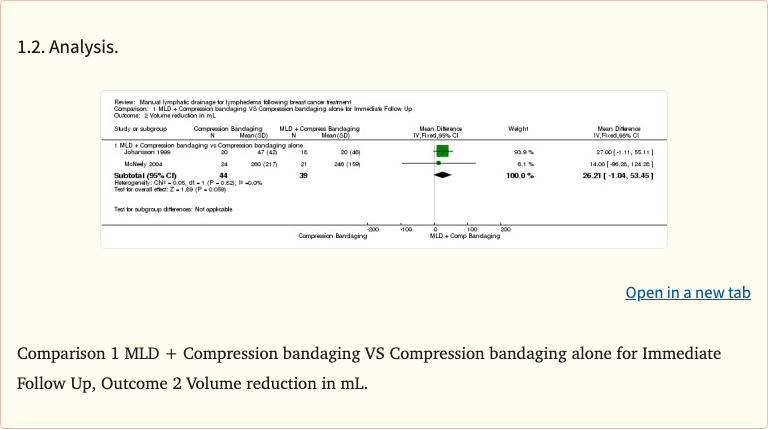 Figure 4
Figure 4
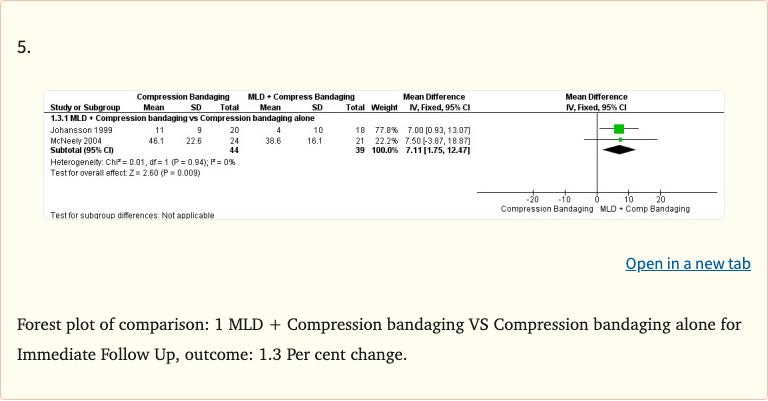 Figure 5
Figure 5
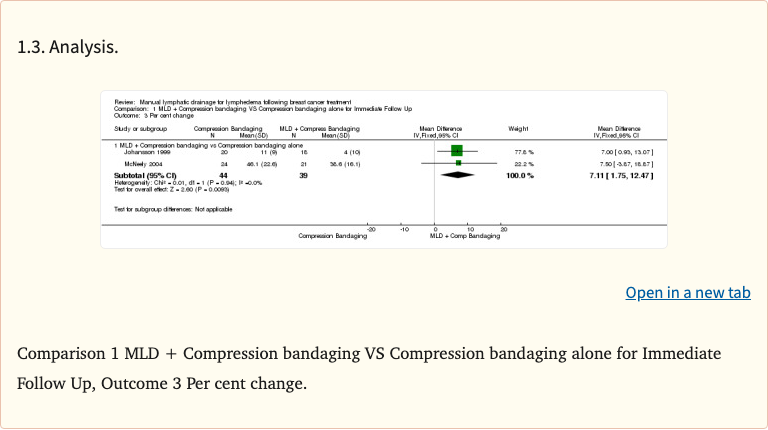 Figure 6
Figure 6
Limitations
- Low quality evidence overall
- Heterogeneous treatment protocols
- Focused on clinical lymphedema population
- May not generalize to healthy individuals
