Key Takeaway
Systematic review finding creatine improves short-term memory and reasoning, with strongest effects under stress conditions like sleep deprivation.
Summary
This systematic review examined the cognitive effects of creatine supplementation in healthy individuals. The researchers analyzed studies measuring various cognitive domains including memory, attention, and executive function.
The key finding was that creatine supplementation improved short-term memory and reasoning/intelligence, with the most pronounced effects occurring under conditions of stress such as sleep deprivation or mental fatigue.
The review suggests creatine's cognitive benefits stem from enhanced brain energy metabolism, as the brain is highly dependent on ATP.
Methods
- Systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- Included healthy individuals across age groups
- Analyzed multiple cognitive domains
- Examined effects under normal and stressed conditions
Key Results
- Improved short-term memory
- Enhanced reasoning and intelligence scores
- Strongest effects under stress/sleep deprivation
- Vegetarians showed larger cognitive benefits
Figures
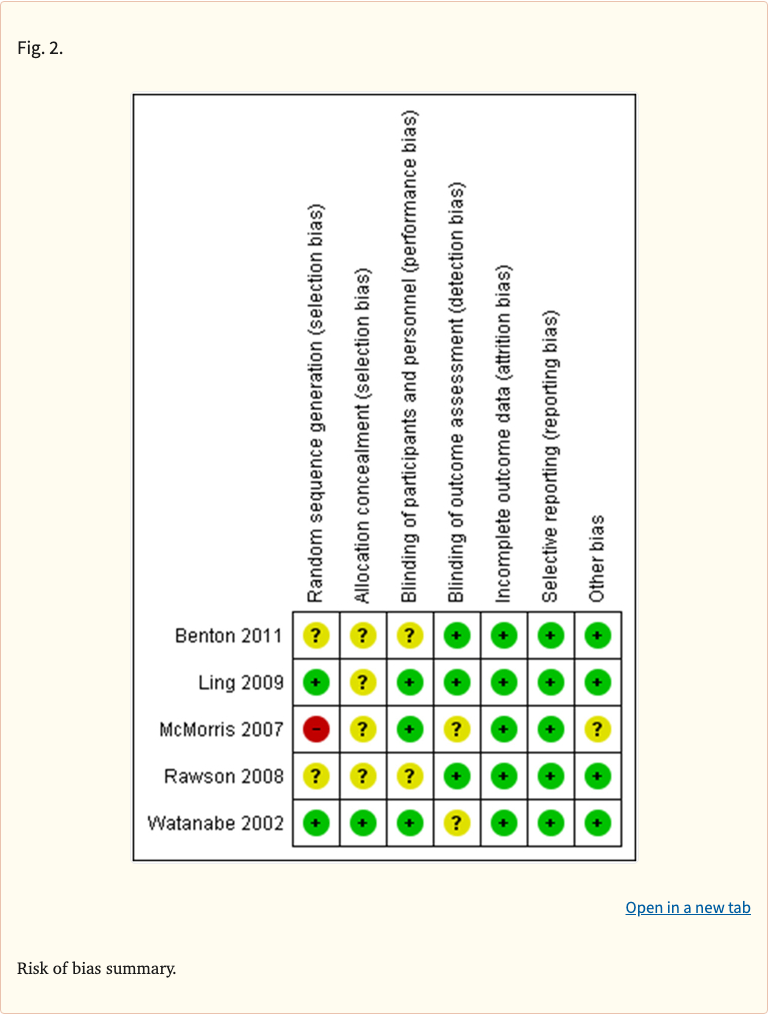 Figure 1
Figure 1
Limitations
- Relatively few studies available
- Heterogeneous cognitive tests used
- Optimal dosing for cognition unclear
- Long-term cognitive effects unknown